Due to its ability to ensure the efficient and continuous transfer of heat across fluids, heat exchanger is a crucial component of industrial systems. Heaters, air conditioners, and energy recovery are only a few of the essential operations they provide for thermal systems. These gadgets, which are used in many different applications, are essential for improving energy efficiency and temperature management. Heat exchangers play an essential role in modern engineering and technology as they enable fluids to exchange heat while retaining their separation. This contributes considerably to the sustainability and functioning of numerous industrial processes.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of heat exchangers, their types, and the underlying principles that govern their functionality.
Definition and Purpose:
Heat exchangers are elaborately engineered devices designed to transmit thermal energy between fluids or between a fluid and a solid surface. Their primary function is the accurate regulation of temperatures in systems or processes, including heating and cooling needs. Heat exchangers are very versatile and are essential components of many industries, including power plants, HVAC systems, refrigeration, chemical processing, and the automobile industry. These components act as cornerstones, enhancing temperature control and enabling effective energy use in a variety of applications vital to contemporary industrial operations.
Types of Heat Exchangers:
Heat exchangers come in various designs, each tailored to meet specific requirements. The common types include:
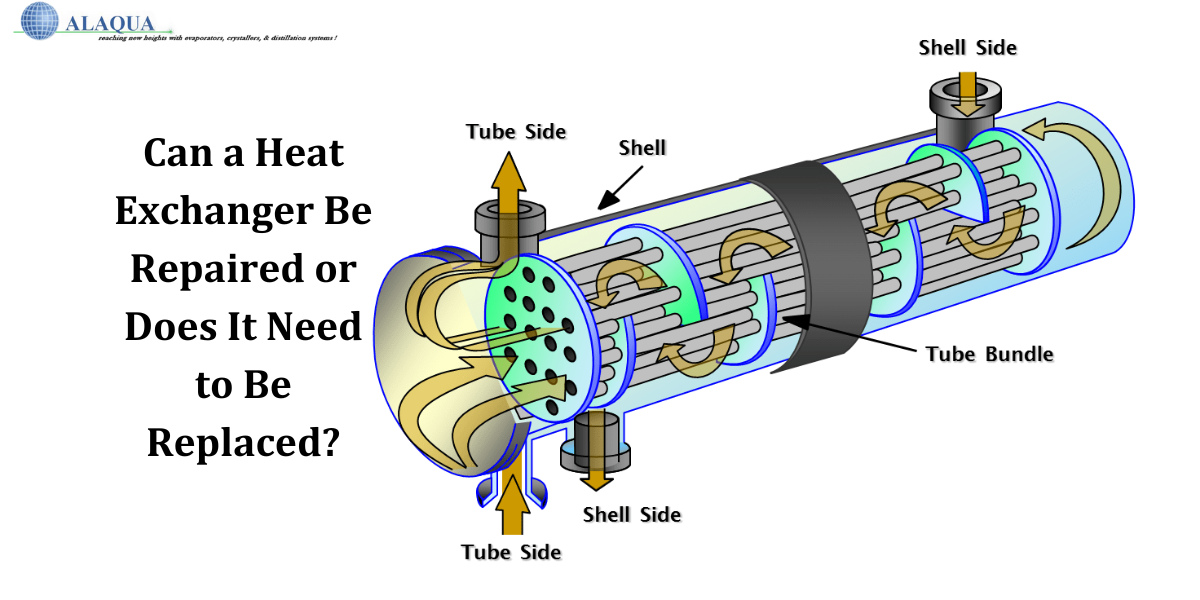
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers:
Thermal engineers use shell and tube heat exchangers, which consist of a cylindrical shell with many tubes within. One liquid flows through the tubes and another surrounds them. They are highly effective in industrial operations and high-pressure applications because of their toughness. Because of the large surface area in the tubes, these exchangers provide effective heat transmission. Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are widely used in a variety of industries, including chemical production and power plants. They are an efficient and adaptable way to exchange thermal energy. This subsequently helps regulate temperature in a wide range of industrial applications.
Plate Heat Exchangers:
Plate heat exchangers are small, effective thermal energy exchange devices. They are made up of several corrugated plates that alternately provide channels for the passage of two fluids. They are perfect for use in refrigeration and HVAC systems because of their efficient heat transmission and maximum surface area design. The turbulent flow that the plates generate is what gives them their adaptability and excellent heat transfer efficiency. Various sectors use plate heat exchangers because they offer a vital solution for temperature control and energy optimization in a range of operations, from industrial to commercial.
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers:
The special equipment that improves heat transfer efficiency is a finned tube heat exchanger. The heat exchange area of these exchangers is increased by the fins—extended surfaces on the tubes. Fins are useful in air-cooling applications, such as radiators in automobiles, to promote heat dissipation. Through an increase in the fluid’s surface area in contact with the surrounding air, the design facilitates effective thermal performance. For applications needing optimal heat transfer capabilities and maximum temperature control, finned tube heat exchangers provide an effective option.
Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers:
Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers are straightforward yet efficient heat-transfer devices made out of two concentric pipes. They are appropriate for small-scale applications requiring less heat transmission because of their simple design. Heat exchange is facilitated by the circulation of fluids between the inner and outer pipes. Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers, despite their straightforward design, is useful in situations where dependability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance are valued. They provide an effective way to meet moderate heat transfer requirements in a variety of industrial processes.
Working Principles:
The fundamental principle governing heat exchangers is the concept of thermal conduction. It is a natural phenomenon for heat to transfer from a warmer to a cooler fluid when they come into contact. Heat exchangers help with this transmission and keep the two fluids from mixing.
The key components influencing heat exchangers include:
Temperature Gradient:
The temperature gradient is a representation of the rate of temperature change over a certain distance. So it determines the direction and intensity of thermal energy flow between two media, making it a crucial parameter in heat transfer. A greater gradient indicates a faster rate of temperature change and, as a result, more heat exchange potential.
Surface Area:
One important component affecting the efficiency of heat transmission is surface area. Greater fluid contact made possible by a bigger surface area in heat exchangers improves the efficiency of thermal energy exchange. To maximize heat transfer rates and raise the general efficiency of heat exchange systems, the surface area must be maximized.
Fluid Flow Rates:
The efficiency of heat transfer in heat exchangers is strongly influenced by fluid flow rates, which are crucial. The carefully regulated flow of fluids through the system guarantees the ideal contact time for efficient heat exchangers. To achieve the required temperature control and maximize the overall performance of heat exchanger units in a variety of industrial applications, flow rates must be balanced and regulated.
Type of Fluids:
The properties of fluids, such as thermal conductivity and specific heat, have a big impact on heat transmission in heat exchangers. So the kind of fluids used in the system has an impact on its overall efficiency; in many industrial applications, fluids with greater specific heat and thermal conductivity provide more efficient heat exchange operations.
To Wrap Up:
In summary, heat exchangers are indispensable devices in thermal engineering, enabling the efficient exchange of heat between fluids while maintaining their separation. So as technology advances, heat exchangers continue to evolve, providing solutions for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Moreover, contributes to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. You can easily find the heat exchanger equipment supplier.
Bajaj Immersion 1500 Watts Water Heater Rod | Nickel Plated Heating| Copper | ISI Certified | 2 Years Warranty | Silver
₹599.00 (as of 20 November, 2024 18:31 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ezee Black Garbage Bags for Dustbin | 90 Pcs | Medium 19 X 21 Inches | 30 Pcs x Pack of 3
₹159.00 (as of 20 November, 2024 18:31 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)GIGAWATTS 10.5 MTR/38 LED String Light 360° Copper Power Pixel 35 Feet Serial Decorative Fairy Lights for Home Diwali Christmas Festival Wedding Party & Garden (Pack of 1, Warm White)
₹89.00 (as of 21 November, 2024 18:32 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Misamo Enterprise PVC Wall Hooks, Pack of 15, Transparent
₹189.00 (as of 20 November, 2024 18:31 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Crompton Arno Neo 15-L 5 Star Rated Storage Water Heater (Geyser) with Advanced 3 Level Safety, National Energy Conservation Award Winner 2023
₹6,299.00 (as of 20 November, 2024 18:31 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Discover more from The General Post
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.