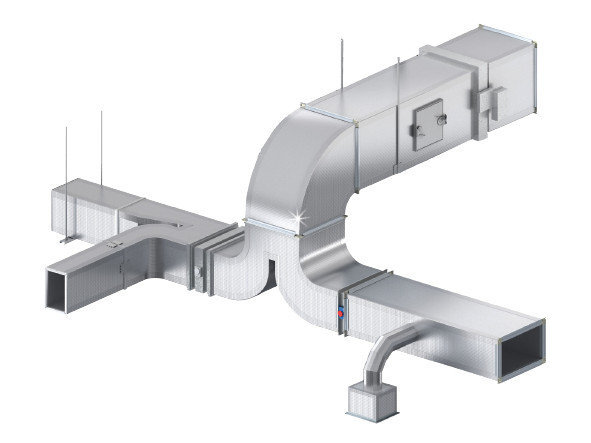
Rectangular ducting is a popular choice in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems due to its various advantages, but it also comes with certain disadvantages. Understanding these can help in making informed decisions about its use in different applications.
Advantages:
Space Efficiency:
Design Flexibility: Rectangular ducts can be designed to fit into tight spaces, making them ideal for buildings with limited ceiling height or other spatial constraints. They can be easily adapted to the architectural layout of a building.
Low Profile: Their flat shape allows them to be installed in shallow spaces, such as above ceilings or in walls, without significantly reducing headroom.
Capacity and Airflow:
Large Air Volume: Rectangular ducts can handle a large volume of air, making them suitable for commercial and industrial applications where high airflow is required.
Custom Sizing: They can be manufactured in custom sizes to meet specific airflow requirements, ensuring optimal performance of the HVAC system.
Installation and Maintenance:
Ease of Installation: The flat sides of rectangular ducts make them easier to handle and install compared to round ducts. They can be easily cut and modified on-site to fit specific dimensions.
Accessibility: The flat surfaces and larger dimensions of rectangular ducts provide easier access for cleaning and maintenance, which is crucial for maintaining indoor air quality.
Aesthetic Integration:
Blending with Structure: Rectangular ducts can be integrated into the building structure in a way that is less noticeable. They can be concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings, providing a cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing look.
Place Your Online Orders: https://www.ductingsuppliesuk.com/shop-online
Disadvantages:
Airflow Efficiency:
Pressure Drop: Rectangular ducts have more surface area in contact with the air, leading to higher friction losses compared to round ducts. This can result in a greater pressure drop and reduced airflow efficiency.
Turbulence: The corners and edges in rectangular ducts can cause air turbulence, which can reduce the efficiency of the airflow and increase energy consumption.
Construction and Material Costs:
Material Usage: Rectangular ducts generally require more material to construct compared to round ducts of the same capacity. This can lead to higher material costs.
Fabrication Complexity: Custom sizes and shapes may require more complex fabrication processes, increasing labor costs and construction time.
Noise and Vibration:
Noise Generation: The flat surfaces of rectangular ducts are more prone to vibration and noise generation. This can be a concern in environments where noise levels need to be minimized, such as offices or residential buildings.
Insulation Needs: To mitigate noise, additional insulation may be required, further increasing the cost and complexity of the installation.
Leakage and Sealing:
Sealing Challenges: The joints and seams in rectangular ducts can be more difficult to seal effectively, leading to potential air leakage. Proper sealing techniques and materials are essential to prevent energy loss and maintain system efficiency.
Conclusion:
Rectangular ducting offers several advantages, such as space efficiency, capacity for large air volumes, ease of installation, and aesthetic integration. However, it also presents challenges related to airflow efficiency, material and construction costs, noise, and sealing. When selecting ducting for an HVAC system, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the building and the application to determine whether rectangular ducts are the best choice. Balancing the advantages and disadvantages will ensure optimal performance, cost-effectiveness, and comfort in the HVAC system.
CASPIAN /// Hike Stainless Steel Customize Sipper Water Bottle (CUS-Matte Black 1 Litre, Set of 1)| Leak Proof Thunder for Fridge Home Office Travel School Kids Boys Girls Adults Sports Gym Yoga
₹299.00 (as of 7 November, 2024 18:25 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rylan 2 in 1 Dumpling Maker Ghughra Momos Maker Machine, Skin Press Mould for Gujiya Ghughra Mould Machine, Kitchen Dumpling Making Tool with Dumpling Puri Maker(Design 1)
₹199.00 (as of 7 November, 2024 18:25 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)IDELLA Soft sillicon Super Absorbent Door Mats (40x60) Bath Mat Anti Skid Quick Drying Bathroom & Water Absorbent Carpets Kitchen Entrance Door Mats (1, Oval R)
₹129.00 (as of 7 November, 2024 18:25 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Skylike 6 fridge storage boxes multipurpose containers for storage fridge storage containers Refrigerator Side Door Organizer for fridge kitchen Fruits, Vegetables Storage Containers- transparent
₹284.00 (as of 7 November, 2024 18:25 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)JIALTO Adhesive Wall Hook 10 Pack Heavy Duty Wall Hooks for Hanging Wall Decor Items Home Decor Items Wall Clock Hanging Hooks Photo Frame Hooks for Wall Without Drilling Nail Hook Key Holder
₹229.00 (as of 7 November, 2024 18:26 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Discover more from The General Post
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.