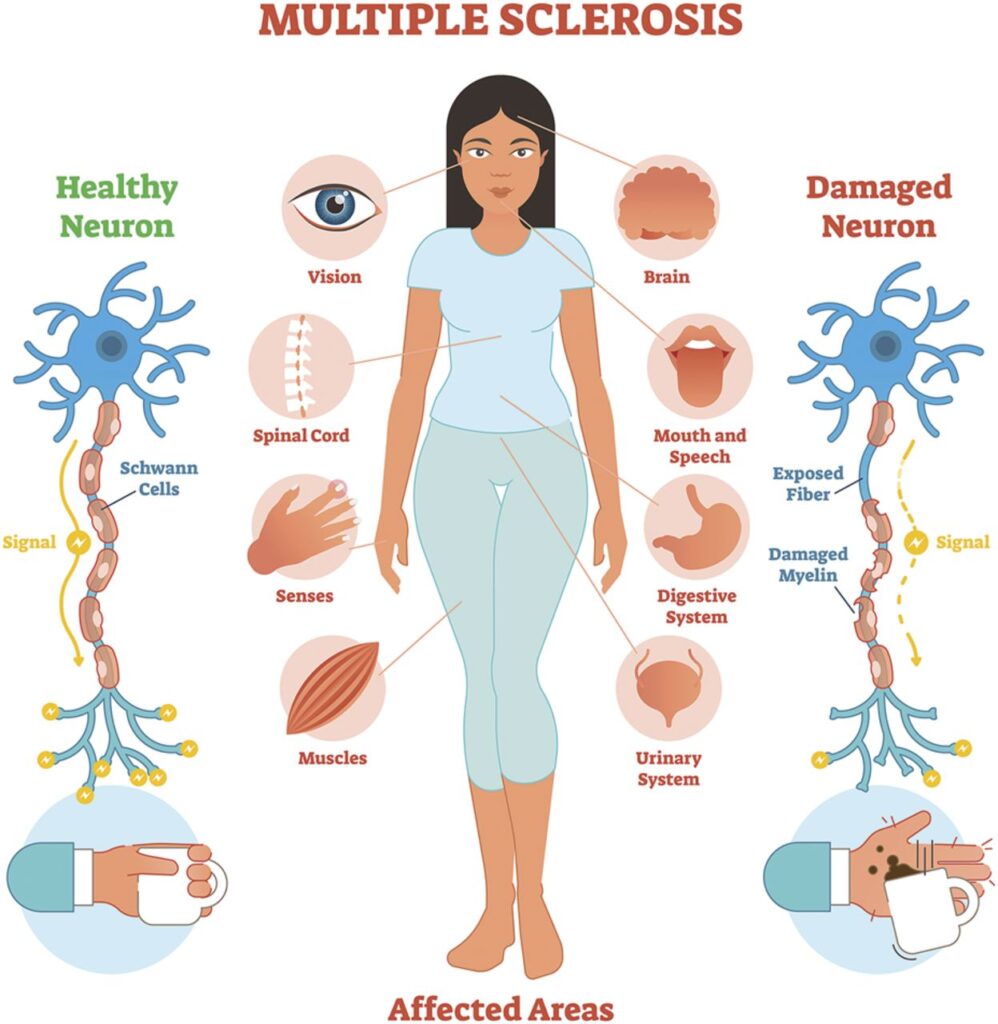
In the United States, around 1 million people are living with multiple sclerosis (MS). Of these, 80-85% of individuals diagnosed with MS have relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), making it the most common subtype. Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Analysis RRMS is characterised by flare-ups or relapses, followed by periods of remission where symptoms improve or disappear entirely. While the exact cause of RRMS remains unclear, it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the central nervous system (CNS), specifically the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibres.
Given its high prevalence and the complex nature of the disease, researchers are emphasizing the development of high-quality, effective drugs to manage RRMS. Currently, available treatments are primarily aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of relapses, slowing disease progression, and managing symptoms. Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS) Drug Pipeline, offering insights into the latest drug developments, pipeline dynamics, trends, segmentation, market growth, and the impact of COVID-19 on the treatment landscape.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/relapsing-remitting-multiple-sclerosis-drug-pipeline-insight/requestsample
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Analysis Overview
The Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline encompasses therapies that are currently under development to manage RRMS. These therapies aim to modify the disease course, reduce inflammation, and promote remyelination — the process of repairing the damaged myelin sheath. The goal is to slow or halt disease progression, prevent relapses, and improve the quality of life for patients living with RRMS.
Currently, disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are the cornerstone of RRMS treatment. These include interferons, monoclonal antibodies, and oral therapies, which help reduce the frequency of relapses and slow the progression of the disease. However, there remains a significant unmet need for more effective treatments that offer better long-term efficacy, fewer side effects, and greater convenience for patients. As a result, the RRMS drug pipeline is rich with innovative approaches, including new drug classes and combination therapies.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/relapsing-remitting-multiple-sclerosis-drug-pipeline-insight
The pipeline also includes drugs that target the underlying mechanisms of RRMS, such as immune modulation, neuroprotection, and remyelination. In addition to DMTs, symptom management treatments are being explored to improve patient outcomes in areas like pain, fatigue, and mobility.
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Dynamics
Several key dynamics are shaping the RRMS Drug Pipeline. These dynamics include advancements in drug mechanisms, the development of targeted therapies, increasing knowledge of disease pathophysiology, and a growing understanding of patient needs.
1. Targeting the Immune System
A central aspect of RRMS is the dysfunction of the immune system, which mistakenly attacks the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibres. The current pipeline of drugs is focusing on modulating the immune system to reduce its attacks on the CNS. The development of B-cell therapies, T-cell therapies, and anti-inflammatory monoclonal antibodies is aimed at either suppressing or modulating the immune response, which plays a key role in the progression of RRMS.
2. Neuroprotection and Remyelination
Another dynamic is the exploration of therapies that promote neuroprotection (to protect nerve cells from damage) and remyelination (the repair of damaged myelin). These approaches aim to address the long-term consequences of RRMS, such as irreversible disability. Agents that promote remyelination are particularly promising as they could help restore lost function and improve long-term outcomes for patients.
3. Oral Therapies and Convenience
Traditionally, RRMS treatments have been injectable or infused, which can be cumbersome and lead to patient non-compliance. As such, there is a shift toward the development of oral therapies that provide greater convenience and improve patient adherence. Oral medications like fingolimod (Gilenya) and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera) have paved the way for the development of new oral drugs, with several promising candidates currently in the pipeline.
4. Improved Safety Profiles
One of the biggest challenges in treating RRMS is balancing efficacy with safety. Some of the existing DMTs can cause significant side effects, such as liver toxicity, infections, and increased risk of malignancy. Therefore, a significant focus of the drug pipeline is to develop drugs that maintain high efficacy while offering improved safety profiles. Newer treatments aim to minimise adverse effects through more targeted action or better patient monitoring.
5. Personalised Medicine
Advances in genetic and biomarker research are allowing for more personalized approaches to MS treatment. By identifying genetic factors and specific biomarkers associated with the disease, researchers aim to develop therapies tailored to individual patients, increasing the likelihood of success and reducing the risk of side effects.
External Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Analysis Trends
Several external trends are influencing the development of drugs for RRMS, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting patient needs.
1. Increased Investment in Research and Development
There is a significant increase in the investment in R&D for RRMS treatments, driven by the growing unmet need for more effective therapies. Pharmaceutical companies, including large players and biotech firms, are focusing on novel drug classes, and there is increasing collaboration between academia, research institutions, and industry to accelerate innovation.
2. Focus on New Drug Classes
There is a trend toward developing new classes of drugs for RRMS, such as S1P modulators, BTK inhibitors, and B-cell depleting agents. These novel therapies offer the potential for better targeting of disease mechanisms and more effective control of relapses and progression.
3. Regulatory Support
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA are offering accelerated approval pathways for promising MS treatments, including fast track and breakthrough designations. This support enables faster access to new therapies for patients in need and encourages pharmaceutical companies to invest in innovative solutions.
4. Patient-Centric Approach
The increasing emphasis on patient-centric care is influencing the development of RRMS drugs. Patients are demanding treatments that not only offer better efficacy but also improved safety and convenience. This has led to a focus on developing oral drugs, as well as therapies that target both disease progression and symptom management.
5. Telemedicine and Digital Health
With the rise of telemedicine and digital health tools, patients with RRMS can now more easily engage in remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and symptom tracking. These technologies are helping to personalise treatment plans and allow for more accurate assessments of treatment outcomes.
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Segmentation
The Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline can be segmented based on various factors, including drug class, stage of development, and patient demographics. Key segments include:
1. Drug Class
- Immunomodulatory Drugs: Including interferons, glatiramer acetate, and S1P modulators.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Targeting specific immune system components like B-cells and T-cells.
- Oral Therapies: Including S1P modulators like fingolimod, and oral formulations of other drugs.
- Neuroprotective Agents: Focused on protecting nerve cells from damage and promoting myelin repair.
- Combination Therapies: Pairing immune modulators with other classes of drugs to improve efficacy and reduce side effects.
2. Stage of Development
- Preclinical: Early-stage drug development focused on discovering new molecules and validating mechanisms of action.
- Phase I: Safety trials involving a small number of healthy volunteers or patients.
- Phase II: Efficacy trials to assess the drug’s ability to modify disease course and reduce relapses.
- Phase III: Large-scale clinical trials to confirm efficacy and safety in diverse patient populations.
- Approved: Drugs that have received regulatory approval for use in clinical practice.
3. Patient Demographics
- Adults: Drugs targeted at the most common age group for RRMS (typically between the ages of 20-40).
- Elderly: Treatment approaches for older patients, who may have comorbidities and different drug tolerances.
- Pediatrics: Although rare, RRMS can also affect children, leading to the development of age-appropriate therapies.
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Growth
The growth of the RRMS drug pipeline has been remarkable in recent years. Advances in drug development, combined with increasing understanding of the disease’s mechanisms, are leading to the creation of more potent and targeted treatments. Several factors contribute to this growth:
- Unmet Medical Need: Despite the availability of existing treatments, many patients still experience breakthrough relapses and disease progression. This has created a strong demand for new, more effective therapies.
- Advances in Immunology: A deeper understanding of the immune system’s role in MS is enabling the development of drugs that can more precisely target immune dysfunction.
- Regulatory Pathways: Accelerated approval processes are helping bring new drugs to market faster, improving the outlook for future therapies.
- Collaborative Research: Increasing collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, universities, and research institutions is fostering innovation and speedier drug development.
Recent Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Market
The RRMS drug pipeline market is expanding rapidly, with several promising drugs nearing approval. Companies such as Celgene, Hoffmann-La Roche, and Hikma Pharmaceuticals are leading the way, with multiple drugs in clinical trials aimed at improving treatment options. The market for RRMS therapies is expected to grow significantly as new treatments enter the market and as more patients seek out effective solutions.
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Scope
The scope of the RRMS drug pipeline extends far beyond the development of traditional disease-modifying therapies. With the focus on immunology, remyelination, and neuroprotection, the scope of treatments is broadening to include therapies that target various aspects of the disease, improving both short-term and long-term outcomes for patients.
Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Drug Pipeline Analysis
The RRMS drug pipeline analysis indicates an exciting future for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. As researchers continue to innovate and explore new approaches to treatment, patients will benefit from a wider range of effective therapies.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the RRMS drug pipeline. On one hand, it slowed some clinical trials due to restrictions on in-person visits and resources being redirected toward COVID-19 treatments. On the other hand, the pandemic has highlighted the need for innovative therapies, pushing the development of oral treatments, digital health tools, and more effective disease-modifying therapies for autoimmune diseases.
Key Players in the RRMS Drug Pipeline
- Celgene: Known for its work in autoimmune diseases and its development of ozanimod, a promising S1P receptor modulator for RRMS.
- Hoffmann-La Roche: Leader in the development of Ocrevus (ocrelizumab), a monoclonal antibody that has shown efficacy in RRMS treatment.
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals: Known for developing oral therapies and treatments that could provide more convenience for RRMS patients.
FAQ
1. What is relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis?
RRMS is the most common form of multiple sclerosis, characterised by periods of relapse followed by remissions where symptoms improve or disappear.
2. How is RRMS treated?
RRMS is typically treated with disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), such as immunomodulators, monoclonal antibodies, and oral medications.
3. What are the latest trends in RRMS drug development?
Current trends include developing targeted therapies, oral drugs, and drugs that promote neuroprotection and remyelination.
4. Who are the key players in the RRMS drug pipeline?
Key players include Celgene, Hoffmann-La Roche, and Hikma Pharmaceuticals, all of which are developing innovative therapies for RRMS.
5. What is the impact of COVID-19 on RRMS treatment development?
COVID-19 has accelerated the development of oral treatments and digital health tools but has also slowed clinical trials due to resource limitations.