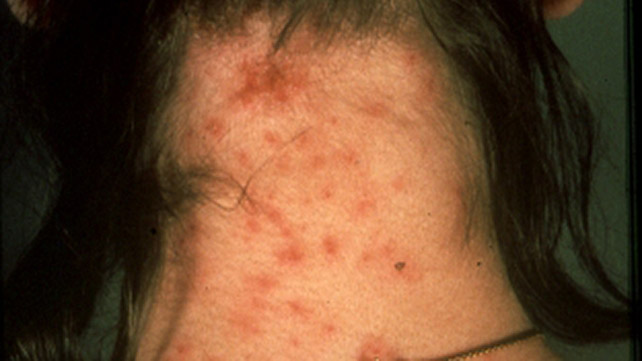
1. Types of Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections are cause by various types of fungi, often thriving in warm, moist areas of the body. The most common types include:
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): This infection affects the feet, particularly the areas between the toes, causing itching, redness, and peeling skin.
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Despite its name, ringworm is not cause by a worm but by a fungus. It presents as a circular, red, and scaly rash with clearer skin in the middle, giving it a ring-like appearance.
- Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris): Common among athletes, jock itch affects the groin area, causing itching, redness, and a ring-shaped rash.
- Yeast Infections (Candidiasis): Caused by the Candida species, yeast infections can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth (thrush) and skin folds, leading to redness, itching, and white patches.
- Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis): This type of infection affects the nails, causing them to become thickened, discolored, and brittle.
2. Symptoms of Fungal Skin Infections
Symptoms of fungal skin infections vary depending on the type of fungus and the location of the infection but generally include:
- Itching and Redness: A common sign of fungal infections, the skin may feel itchy, red, and irritated.
- Scaling and Cracking: Infections like athlete’s foot often cause the skin to peel, crack, and develop scales.
- Discoloration and Rash: The appearance of red, white, or dark patches on the skin or a ring-shaped rash is a telltale sign of infections like ringworm or candidiasis.
- Blisters or Pustules: Some fungal infections may lead to the formation of small blisters or pustules on the affected skin.
3. Treatment Options for Fungal Skin Infections
Treating fungal skin infections involves a combination of antifungal medications, proper hygiene, and sometimes home remedies. Here are some common treatments:
- Topical Antifungal Creams and Ointments: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, like clotrimazole or miconazole, are often the first line of treatment. They are applie directly to the affect area and help eliminate the fungus.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: For more severe infections, oral antifungals such as fluconazole or terbinafine may be prescribed by a healthcare provider to effectively treat the infection.
- Cephalexin: Although Cephalexin is an antibiotic primarily used for bacterial infections, it may be prescribed in combination with antifungal treatments if there is a secondary bacterial infection complicating the fungal infection.
- Keeping the Skin Clean and Dry: Regularly washing the affected area with mild soap and water and keeping it dry can prevent the infection from spreading and speed up recovery.
- Home Remedies: Applying natural remedies like tea tree oil or diluted apple cider vinegar may help alleviate symptoms, though they should be used with caution and in consultation with a healthcare provider.
4. Preventing Fungal Skin Infections
Prevention is key when it comes to fungal infections. Some effective strategies include:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash and dry areas prone to moisture, such as feet and groin, to prevent fungal growth.
- Wear Breathable Fabrics: Opt for cotton or moisture-wicking clothing to reduce sweat accumulation, which creates an ideal environment for fungi.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, clothing, or shoes, as fungal infections can spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Use Antifungal Powders: Applying antifungal powders to feet or other prone areas can help prevent fungal growth.
5. When to See a Doctor
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if:
- The infection does not improve with over-the-counter treatments within a few weeks.
- Symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear.
- You have a weakened immune system or other underlying health conditions that may complicate treatment.
Conclusion
Fungal skin infections, while common, are often manageable with the right combination of treatments, including antifungal medications and proper skin care. Cephalexin may be used in cases where a bacterial infection is also present. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment and prevent the infection from recurring.